Differences Between AI and Machine Learning, and Why it Matters
Unfortunately, some tech organizations are deceiving customers by proclaiming using AI on their technologies while not being clear about their products’ limits – Roberto Iriondo – Oct 15, 2018
Image Credits: IoT World Today
Recently, a report was released regarding the misuse from companies claiming to use artificial intelligence [29] [30] on their products and services. According to the Verge [29], 40% of European startups that claimed to use AI don’t actually use the technology. Last year, TechTalks, also stumbled upon such misuse by companies claiming to use machine learning and advanced artificial intelligence to gather and examine thousands of users’ data to enhance user experience in their products and services [2] [33].
Unfortunately, there’s still a lot of confusion on within the public and the media regarding what truly is artificial intelligence [44], and what truly is machine learning [18]. Often the terms are being used as synonyms, in other cases these are being used as discrete, parallel advancements, while others are taking advantage of the trend to create hype and excitement, as to increase sales and revenue [2] [31] [32] [45].
Below we will go through some main differences between AI and machine learning.
What is machine learning?

What is Machine Learning | Tom M. Mitchell, Machine Learning, McGraw Hill, 1997 [18]
Quoting Interim Dean at the School of Computer Science at CMU, Professor and Former Chair of the Machine Learning Department at Carnegie Mellon University, Tom M. Mitchell:
A scientific field is best defined by the central question it studies. The field of Machine Learning seeks to answer the question:
“How can we build computer systems that automatically improve with experience, and what
are the fundamental laws that govern all learning processes? [1]”
Machine learning (ML) is a branch of artificial intelligence, and as coined and defined by Computer Scientist and machine learning pioneer [19] Tom M. Mitchell: “Machine learning is the study of computer algorithms that allow computer programs to automatically improve through experience.” [18] — ML it’s one of the ways we expect to achieve AI. Machine learning relies on working with small to large data-sets, by examining and comparing the data as to find common patterns and explore nuances.
For instance, if you provide a machine learning model with a lot of songs that you enjoy, along their corresponding audio statistics (dance-ability, instrumentality, tempo or genre), it will be able to automate (depending of the supervised machine learning model used) and generate a recommender system [43] as to suggest you with music in the future that (with a high percentage of probability rate) you’ll enjoy, similarly as to what Netflix, Spotify and other companies do [20] [21] [22].
In a simple example, if you load a machine learning program with a considerable large data-set of x-ray pictures along their description (symptoms, items to consider, etc.), it will have the capacity to assist (or perhaps automatize) the data analysis of x-ray pictures later on. The machine learning model will look at each one of the pictures in the diverse data-set, and find common patterns found in pictures that have been labeled with comparable indications. Furthermore, (assuming that we use a good ML algorithm for images) when you load the model with new pictures it will compare its parameters with the examples it has gathered before in order to disclose to you how likely the pictures contain any of the indications it has analyzed previously.
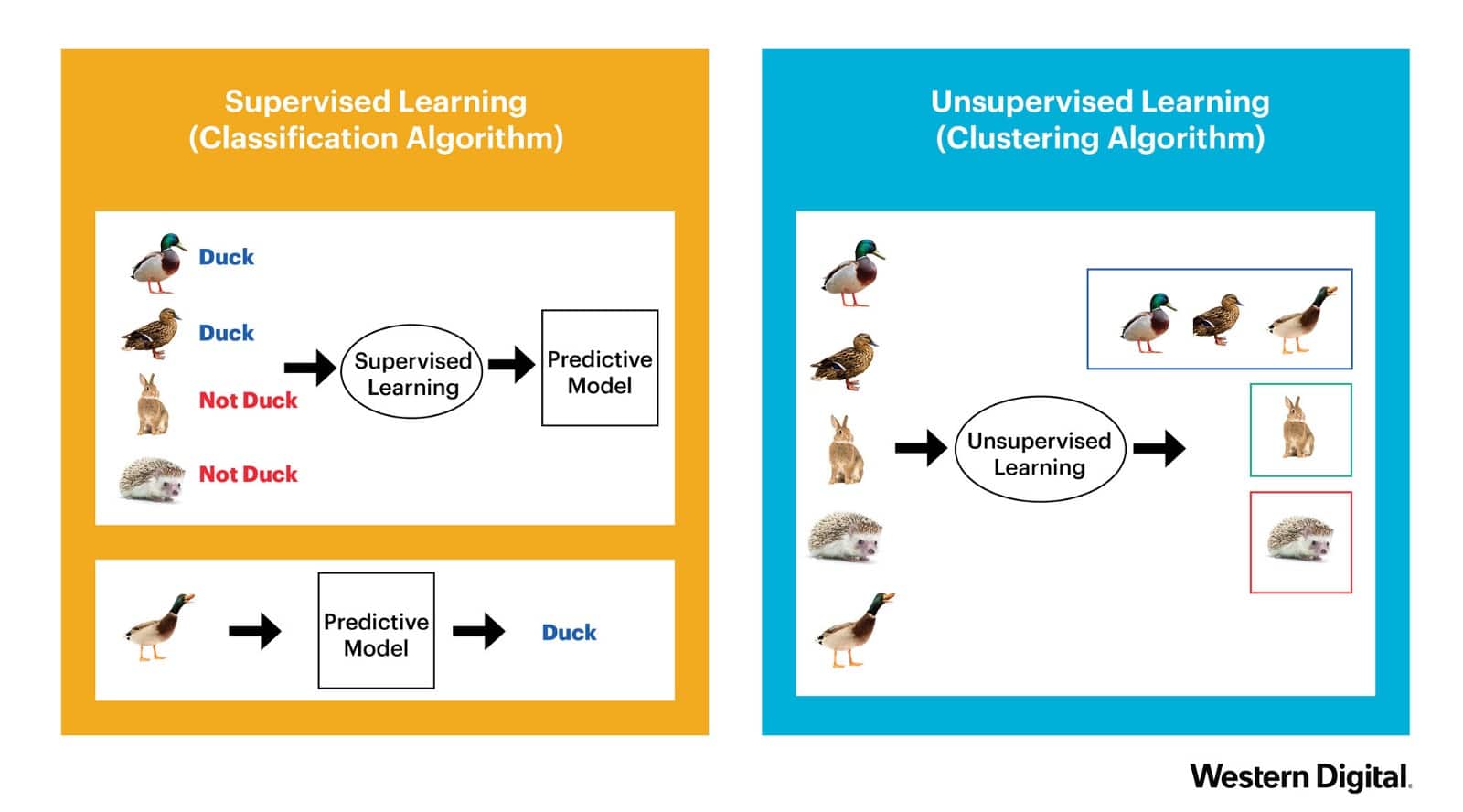
Supervised Learning (Classification/Regression) | Unsupervised Learning (Clustering)
| Credits: Western Digital [13]
The type of machine learning from our previous example is called “supervised learning,” where supervised learning algorithms try to model relationship and dependencies between the target prediction output and the input features, such that we can predict the output values for new data based on those relationships, which it has learned from previous data-sets [15] fed.
Unsupervised learning, another type of machine learning are the family of machine learning algorithms, which are mainly used in pattern detection and descriptive modeling. These algorithms do not have output categories or labels on the data (the model is trained with unlabeled data).
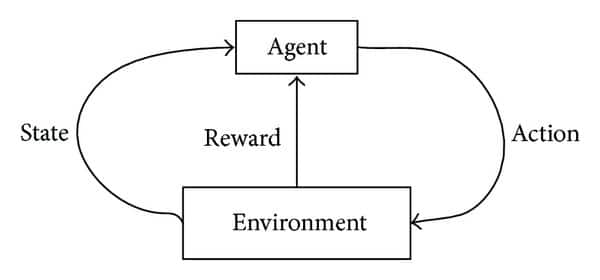
Reinforcement Learning | Credits: Types of ML Algorithms you Should Know by David Fumo [3]
Reinforcement learning, the third popular type of machine learning aims at using observations gathered from the interaction with its environment to take actions that would maximize the reward or minimize the risk. In this case the reinforcement learning algorithm (called the agent) continuously learns from its environment using iteration. A great example of reinforcement learning are computers reaching super-human state and beating humans on computer games [3].
Machine learning is mesmerizing; particularly its advanced sub-branches, i.e. deep learning and the various types of neural networks. In any case, it is “magic” (Computational Learning Theory) [16], regardless of whether the public at times have issues observing its internal workings. In fact, while some tend to compare deep learning and neural networks to the way the human brain works, there are important differences between the two [2] [4] [46].
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
The AI Stack, Explained by Professor and Dean, School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University, Andrew Moore | Youtube [14]
Artificial intelligence on the other hand, is exceptionally wide in scope. According to Andrew Moore [6] [36] [47], Former-Dean of the School of Computer Science at Carnegie Mellon University, “Artificial intelligence is the science and engineering of making computers behave in ways that, until recently, we thought required human intelligence.”
That is a great way to define AI in a single sentence; however, it still shows how broad and vague the field is. Fifty years ago, a chess playing program was considered a form of AI [34], since game theory, along game strategies were capabilities that only a human brain could perform. Nowadays, a Chess game would be considered dull and antiquated, due to the fact that it can be found on almost every computer’s OS [35], therefore, “until recently” is something that progresses with time [36].
Assistant Professor and Researcher at CMU, Zachary Lipton clarifies on Approximately Correct [7], the term AI “is aspirational, a moving target based on those capabilities that humans possess but which machines do not.” AI also includes a considerable measure of technology advances that we know. Machine learning is only one of them. Prior works of AI utilized different techniques, for instance, Deep Blue, the AI that defeated the world’s chess champion in 1997, used a method called tree search algorithms [8] to evaluate millions of moves at every turn [2] [37] [52] [53].
Example of solving the Eight Queens puzzle using Depth First Search |
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence | how2Examples
AI as we know it today is symbolized with Human-AI interaction gadgets by Google Home, Siri and Alexa, by the machine learning powered video prediction systems that power Netflix, Amazon and YouTube. These technology advancements are progressively becoming important in our daily lives. In fact, they are intelligent assistants that enhance our abilities as humans, and professionals — making us more and more productive.
In contrast to machine learning, AI is a moving target [51], and its definition changes as its related technological advancements turn out to be further developed [7]. Possibly, within a few decades, today’s innovative AI advancements will be considered as dull as flip-phones are to us right now.
Why do tech companies tend to use AI and ML interchangeably?
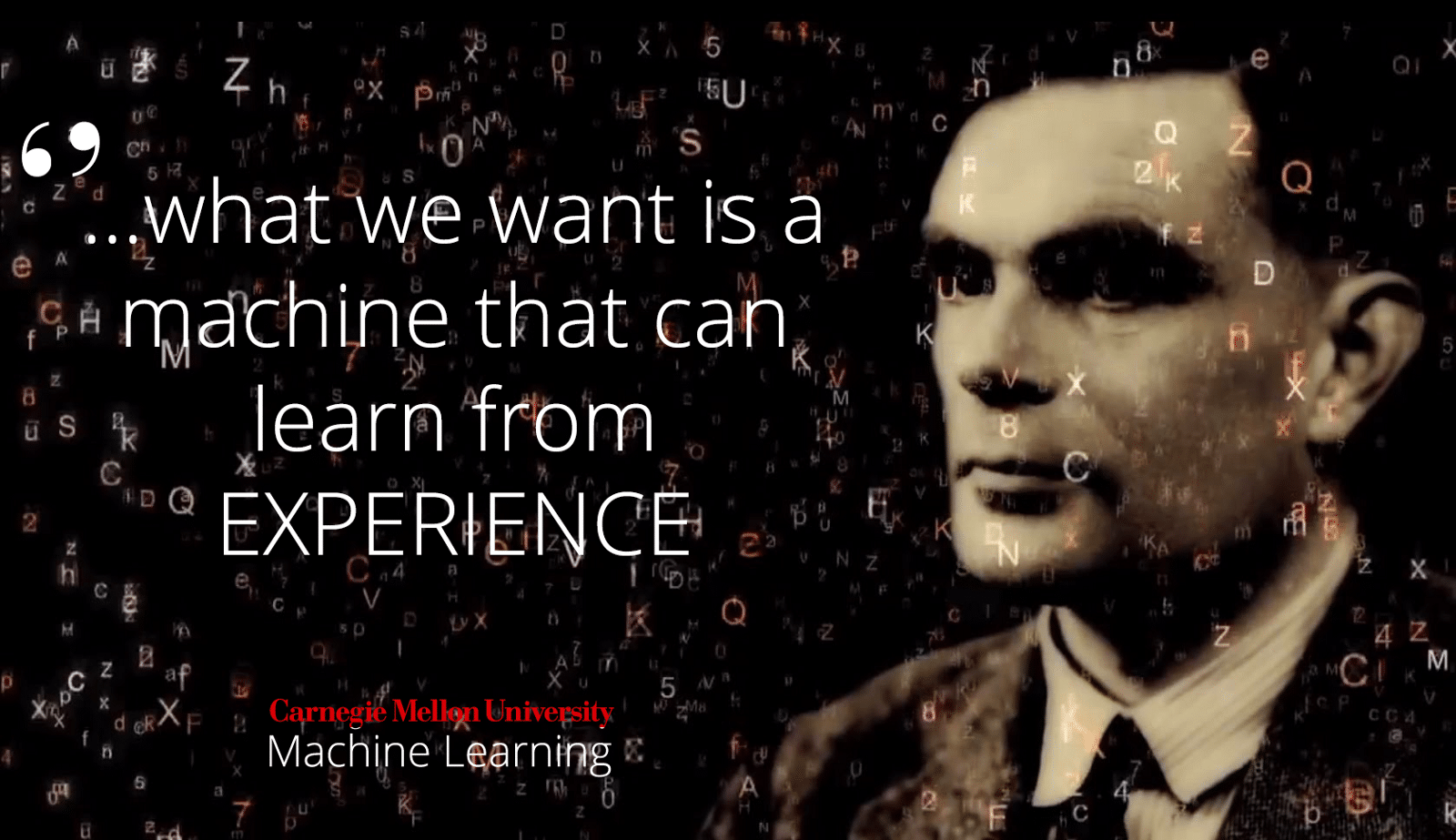
“… what we want is a machine that can learn from experience.” ~ Alan Turing
The term “artificial intelligence” came to inception in 1956 by a group of researchers including Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon [9], Since then, AI’s industry has gone through many fluctuations. In the early decades, there was a lot of hype surrounding the industry, and many scientists concurred that human-level AI was just around the corner. However, undelivered assertions caused a general disenchantment with the industry along the public and led to the AI winter, a period where funding and interest in the field subsided considerably [2] [38] [39] [48].
Afterwards, organizations attempted to separate themselves with the term AI, which had become synonymous with unsubstantiated hype, and utilized different terms to refer to their work. For instance, IBM described Deep Blue as a supercomputer and explicitly stated that it did not use artificial intelligence [10], while it actually did [23].
During this period, a variety of other terms such as big data, predictive analytics and machine learning started gaining traction and popularity [40]. In 2012, machine learning, deep learning and neural networks made great strides and started being utilized in a growing number of fields. Organizations suddenly started to use the terms machine learning and deep learning to advertise their products [41].
Deep learning started to perform tasks that were impossible to do with classic rule-based programming. Fields such as speech and face recognition, image classification and natural language processing, which were at early stages, suddenly took great leaps [2] [24] [49], and on March, 2019–three the the most recognized deep learning pioneers won a Turing award thanks to their contributions and breakthroughs that have made deep neural networks a critical component to nowadays computing [42].
Hence, to the momentum, we are seeing a gearshift back to AI. For those who had been used to the limits of old-fashioned software, the effects of deep learning almost seemed like “magic” [16], especially since a fraction of the fields that neural networks and deep learning are entering were considered off limits for computers. Machine learning and deep learning engineers are earning skyward salaries, even when they are working at non-profit organizations, which speaks to how hot the field is [50] [11].
Source: Twitter | GPT-2 Better Language Models and Their Implications, Open AI
Sadly, this is something that media companies often report without profound examination, and frequently go along AI articles with pictures of crystal balls, and other supernatural portrayals. Such deception helps those companies generate hype around their offerings [27]. Yet, down the road, as they fail to meet the expectations, these organizations are forced to hire humans to make up for the shortcomings of their so-called AI [12]. In the end, they might end up causing mistrust in the field and trigger another AI winter for the sake of short-term gains [2] [28].